Top 25 SEO Terms Every Beginner Should Know

It takes more than reading a blog post to fully understand how to drive more traffic to your website. It takes a clear understanding of search engine optimization (SEO) and all its components, which can be confusing.
To help those new to SEO get acquainted with the challenge, we have comprised a list of the terms we think every SEO beginner should know. It’s not everything about SEO, but it is a start.
Here are the top 25 SEO terms every beginner should know:
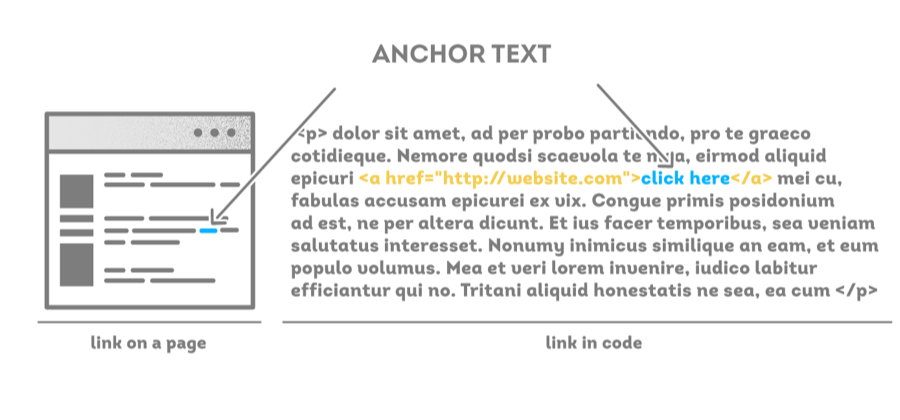
1. Anchor Text:
When one hyperlinks a website into a body of the text the word they attach the link to is called an anchor text. A user clicks on an anchor text for it to redirect them to a different webpage. This is important for SEO practitioners (see what we did there?) because search engines look for these links to determine which are more authoritative than the others.
Authoritative links are the ones search engines find to be quality and to add the most value to users; we’ll discuss this more later on.
Tip: Do not abuse the same anchor text over and over again. This can discredit your page and harm your search results.
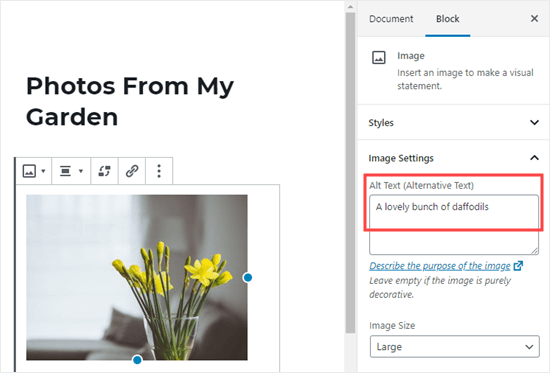
2. Alt Attribute Text (or Alt Text):
Have you ever searched for an item and had an ad with a photograph of the item appear? If you have, then you’ve seen alt text in action.
Alt text refers to the text description of an image that signifies what the image contains. You cannot see the alt text when you look at a photo because it is hidden in the backend of the webpage where the photo is placed.
Alt-text is an effective way to boost your search engine ranking because it allows images on your website to be found during a search.
3. Authority:
Authority refers to a page’s ability to rank high in search engine results.
Five factors are considered in authority rank:
- Age of the page
- Page’s traffic trends
- Backlinks profile
- Quality of page content
- Technical SEO (site speed, schema, etc)
These five reasons help explain why “.edu” and “.gov” websites have higher authority over other pages, like “.com” or “.net.”
4. Bots:
Bots are programs designed to index, collect and analyze website information website faster than a human can. It’s estimated that bots make up 60% of online traffic. As SEO practitioners, we can use bots to quickly gather and analyze information, of our own website and others. Bots also allow for updated content to immediately be shared with the online community.
However, there are helpful bots and harmful bots.
Read more about the difference between the two.
5. Title Tag:
Along with being an HTML element, title tags are crucial for SEO. They help companies accurately describe what their websites contain on search result pages and browser pages. Optimizing title tags for each page allows, users and search engines to quickly gauge the content it includes, allowing pages to be easily linked and ranked.
6. Meta Description:
A meta description follows a title tag in terms of description of a page. It is a sentence or two that describes briefly what that page or website contains.
The more relevant a meta description is to a search query, the more likely it will appear in the search results page, below the page title. An accurate and SEO-friendly meta description will keep your page relevant through the millions of searches happening every minute.
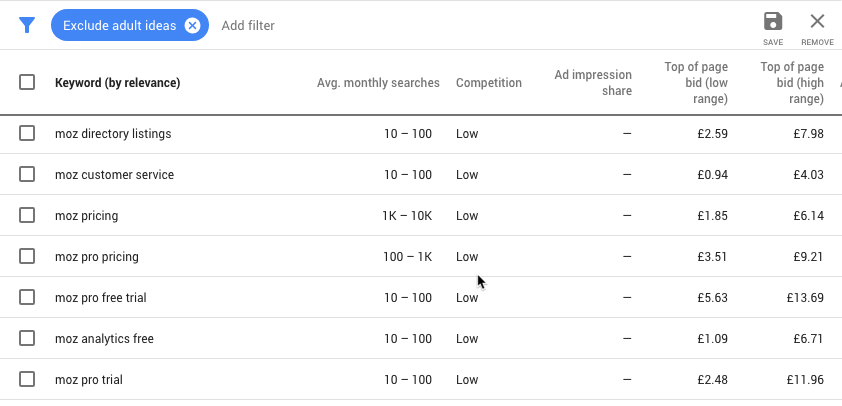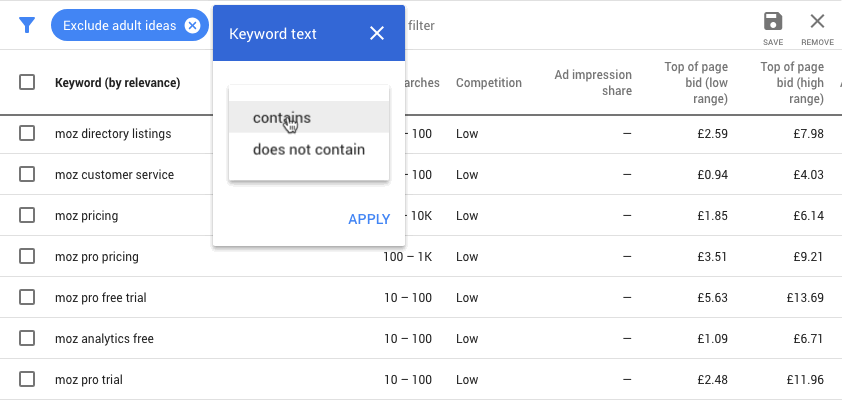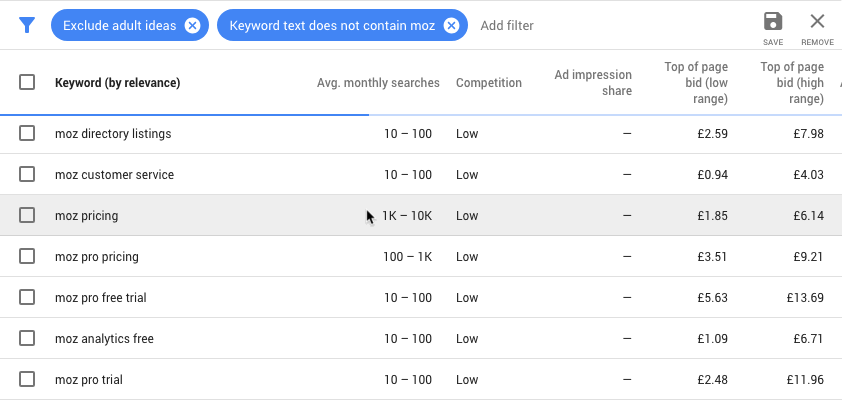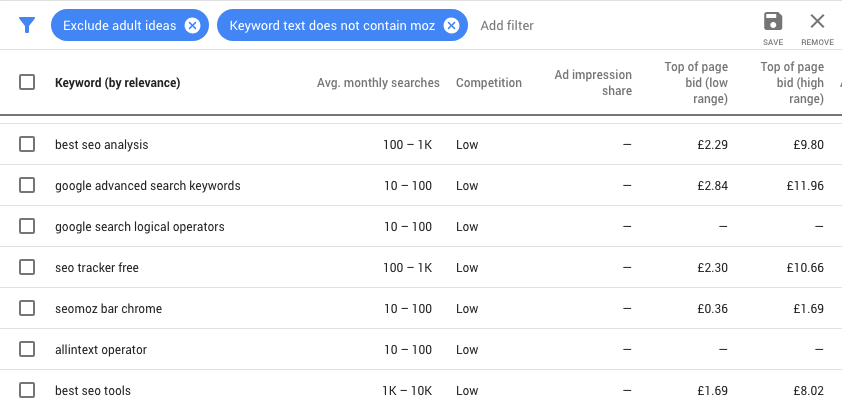
7. Keyword:
As simple as keywords might be, they are incredibly important to SEO.
Keywords are the words or phrases on the website that allow it to be found. For example, if you wanted to find this blog via search engine results, the keywords might be something like “SEO Terms” or “ChatterBuzz Media Blog.” Notice these are not creative titles, yet are precise and describe exactly what the page contains. Keywords that are vague or that yield too many results are ineffective.
Resources like Google Keyword Planner will help you determine which keywords you should target.
8. Long Tail Keyword:
As they name implies, long tail keywords are keywords, just longer. They contain usually three to four words that are commonly used during search.. For this blog post, a good long tail keyword might be “Top 25 SEO Terms” as opposed to just “SEO Terms.” Using the longer version allows you to better target users who are overwhelmed with too many options from a shorter keyword.
Example: This Behavioral & Mental Health Marketing Guide from C4 consulting ranks for the long tail keyword “marketing strategies for mental health services”.
9. Keyword Density:
Keyword density refers to the number of times a keyword appears on a webpage compared to the total words. While this used to be an easy way for pages to rank higher, new search engine algorithms have made this tactic almost useless. However, we can use the same keyword density-measuring tactics to make sure we are not overusing the same keywords on our page.
10. Domain Rank or Domain Authority:
Domain rank or domain authority refers to how well a whole domain will rank on search engine results. It is calculated by a combination of link metrics: linking root domains, number of total links and others on a 100-point scale. This measurement then can be interpreted to see how one website compares to others.
It is one of the most important numbers known to SEOs. The greater your DA, the more likely you are to have strong traffic and high rank.
- Domain authority is based on numerous factors. Primarily, however, these are link profile factors such as how many backward links are pointing to your website and how authoritative those sites are.
- It is very difficult to gain a DA number of 100. Sites like Facebook and Google have it, so don’t be disappointed if you never hit 100. Once you start achieving 50+ going up this scale will get harder and harder.
- DA is difficult to influence directly. You can’t change your DA score like you can change your meta tags.
11. Domain Trust:
Domain trust is a measurement of a website’s links from other trusted websites. These websites include those with a “.edu” or “.gov” ending, as mentioned earlier. If your website has links from some of these pages, it will be seen as more trusted by the search engine. In the image below, you can see websites gaining domain trust through links from berkeley.edu.
12. Page Rank or Page Authority:
Also on a 100-point scale is the measurement of page rank or page authority. Instead of ranking how a whole domain will rank in search engine results, this is a metric of how an individual page will rank in the results. The inherent relationship between page rank and domain rank is why each page on a website should be SEO optimized.
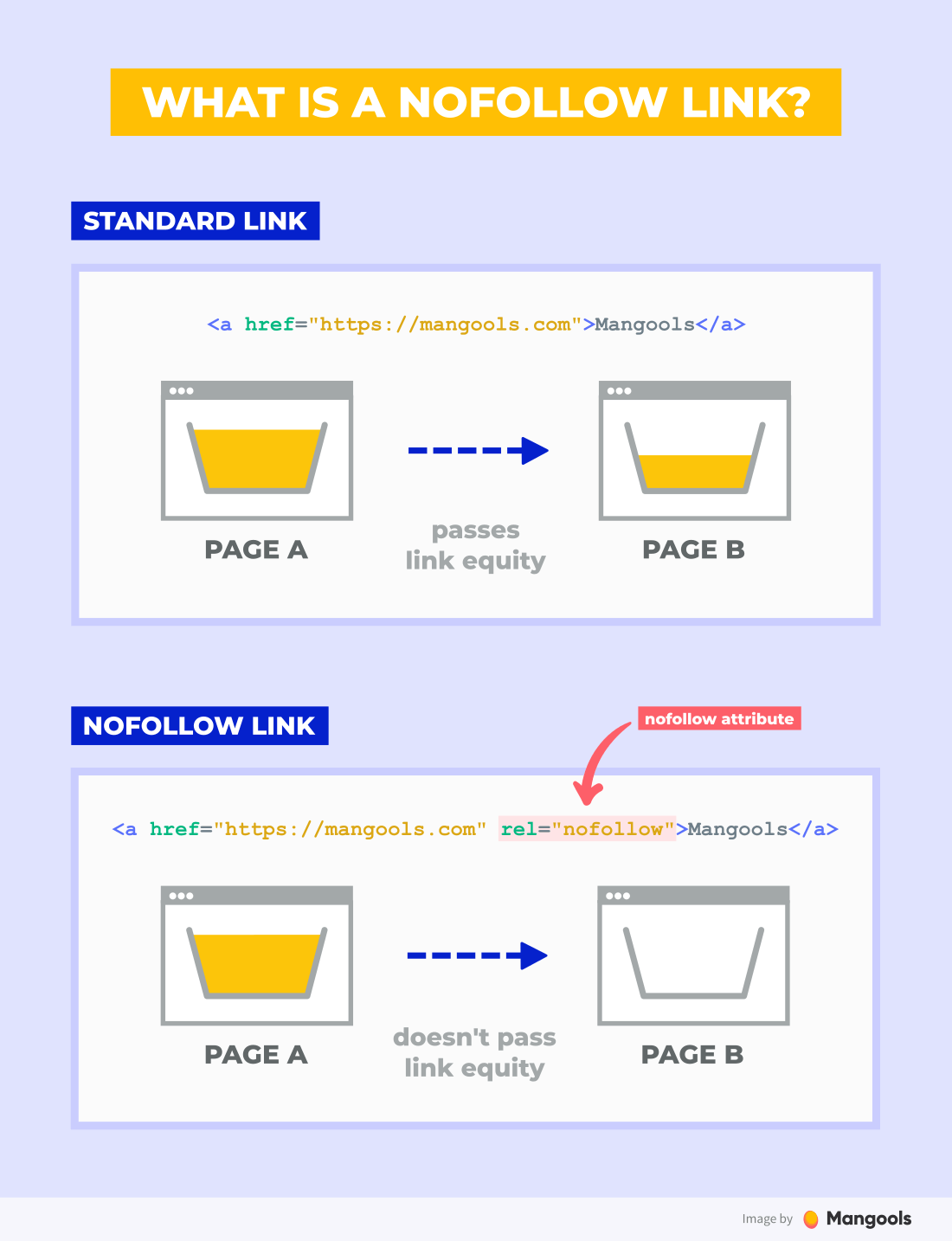
13. Do Follow and No Follow:
These terms refer to a page’s attribute to pass or not pass on link authority to linking websites. As noted before, the more links a website has, the better it ranks. However, when a website has a “No Follow” attribute listed, it does not pass that authority back to the linking website. Websites such as Wikipedia have a No Follow attribute along with 90% of blog comments out there. It sends spammers a message that you will keep you from accidentally passing PageRank on to lower-quality “neighbors” on the web.
14. 301 Redirect:
A 301 redirect refers to the method a website uses to tell a search engine that a page location has permanently moved somewhere else on the website. We can use this redirect to pass on link authority or ranking power to the new page. However, it’s also important to note that 301 redirects may take anywhere from one day to one month for a search engine to pick it up.
15. Canonical URL:
Often, a page’s content might become indexed on other places on the website. This can, in turn, create duplicates of content on the same website. However, the canonical url is always the single most authoritative version. When creating links and making sure a website is SEO optimized, we have to make sure the canonical URL is used.
16. Headings:
Headings are another HTML tag that allows for content to become SEO optimized. Tags range from H1 to H6, with the lower number tags being the most important. When creating a page, you should only have one H1 tag, followed by other tags to structure the page as a whole.
17. Inbound Links:
Inbound links are the links from one website that point back to yours. At a glance, inbound links are more important than outbound links because they show that your website is being linked to across the Internet.
18. Outbound Links:
Outbound links are places where you link to other sites.While outbound links are not inherently important, you can still link from to sites with higher authority to possibly increase your search rank. Some search engines calculate rank with outbound links, and some websites might link back to yours if you link to them. So it could be a win-win situation.
19. SERP:
SERP stands for Search Engine Results Page, or the page where results are shown for a search query. On a SERP, you can analyze a great amount of information: such as keywords used, title and meta descriptions attributes, and other SEO related metrics with browser plug-ins.
20. Breadcrumb Navigation:
Breadcrumb navigation is a navigational technique used to help search engines and users understand the relationship between pages. It identifies where you are on the website and what is related to the page you are on. An example for this blog might look something like the two examples below:
Home > Blog > Top 25 SEO Terms
21. Sitemap:
A sitemap for a website is a file where you can list the pages of a website and attributes if they are accessible to crawlers. It’s important to optimize a website’s sitemap in order for search engine crawlers to accurately find and rate your site.
22. Backdoor Linking:
Backdoor linking is a simple process at a glance but can be very confusing. Essentially, it is posting a link on one website that links back to yours. It can also entail posting a comment on a blog or being listed in a directory. However, to create a worthy backlink, you have to make ensure the following: it has value added content, the content is easy to find and it has a long shelf life. This way you know your backlink will remain on the desired website and will drive traffic back to you. To identify where your site’s backlinks are, you can use tools such as https://ahrefs.com/ and https://www.spyfu.com/.
23. Doorway Linking:
Doorway Links, or Doorway Pages, are forms of web spam on search engine queries. They are also generic and are very often created to mimic the success of other links. They have less prominence today than a couple of years ago because Google and other search engines have reworked their algorithm to avoid them.
Since they are created for particular phrases and search engines, not humans, doorway links may not count towards some search engine rankings. However, they can still drive traffic to your website through a “bridge.”
24. Deep Link:
A deep link refers to a link on your page that links to another page on your site. This simply drives traffic from one page to another and has no direct correlation to SEO. Deep links are used with a newer piece of content on your web page that links to older content so the newer content will rank higher in search.
25. Index or No Index:
Index or No Index refers is when you direct a search engine to either index or not index the page. Basically, with a “no index” HTML tag, a search engine can find our page, but a human cannot through search engine means. Instead, we can directly link a user to a page that is “no index” if we want them to visit the page. Pages that should include a “no index” tag include employee-only pages, promotion pages, and completion pages.
In Summary
Again, these terms do not cover everything SEO entails but do provide a quick umbrella overall. With these terms in your pocket, you should now understand some of the intricacies that go into researching and analyzing SEO.
Once you master these top 5 SEO terms, you are on your way to building better organic search results – for your website and your bottom line.


















